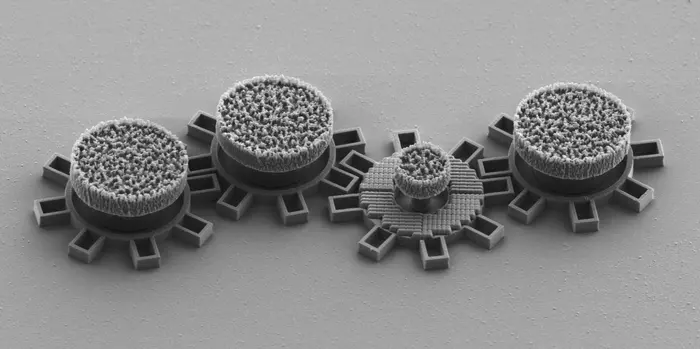
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have unveiled a groundbreaking invention: the world’s “smallest on-chip motor,” small enough to fit inside a single strand of human hair.
This revolutionary micromotor uses light-powered gears, solving a decades-old challenge in micromachine development.
Gears are essential in countless technologies—from clocks and cars to robots and wind turbines. For more than 30 years, engineers have struggled to miniaturize gears beyond the 0.1-millimeter scale due to limitations in building mechanical drive trains.
The Gothenburg team overcame this barrier by abandoning traditional mechanics in favor of laser light-driven motion.
“This is a fundamentally new way of thinking about mechanics on a microscale. By replacing bulky couplings with light, we can finally overcome the size barrier,” explained Gan Wang, lead author of the study and researcher in soft matter physics at the University of Gothenburg.
How the Light-Powered Motor Works
The micromotor is built on a silicon chip using optical metamaterials—tiny, engineered structures that manipulate light at the nanoscale. When a laser shines on the metamaterial gears, the light makes them spin with remarkable precision.
- Speed control is achieved by adjusting the intensity of the laser.
- Rotation direction can be instantly switched by changing the laser’s polarization.
This contactless method eliminates the need for physical connections, making the technology highly scalable.
“We have built a gear train where a light-driven gear sets the entire chain in motion. These gears can convert rotation into linear motion, perform periodic movements, and even control microscopic mirrors to deflect light,” Wang added in the press release dated September 18.
A Leap for Future Technologies
Because the motors can be integrated directly onto chips and powered by light, they open doors to a wide range of applications—from next-generation sensors and optical systems to advanced nanorobotics and medical devices.
This innovation marks a major milestone in nanotechnology and micro-mechanics, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with light-powered machines.